What are you looking for?
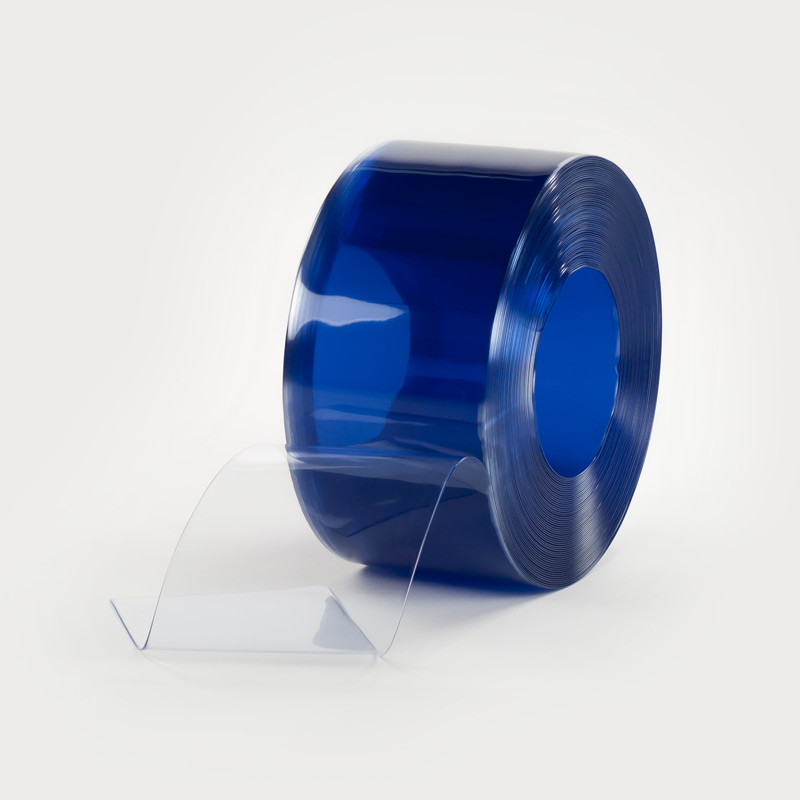
Anti-UV PVC

| High resistance to UV |
| Thermal insulation |
| Transparency/clarity |
| Long durability |

| Impact & scratch resistance |

| Environment friendly & recyclable |
Formats
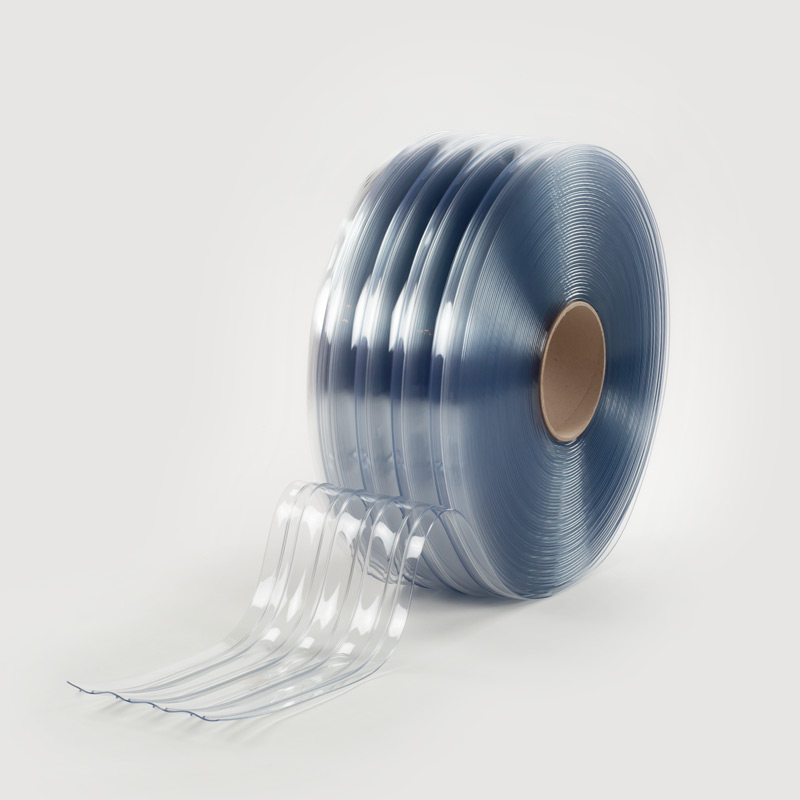
- Rolls, strips, curtains, panels and films
- Ribbed, reinforced, rounded edges, matt surface.
| Min | Max | |
| Width | 75 mm | 2.2 m |
| Thickness | 0.3 mm | 12 mm |
| Length | 20 m | 100 m |
About UV resistant PVC
Anti-UV PVC is a flexible PVC range that has anti-UV properties for added protection from ultraviolet light.
The specific anti-UV additive, included in the PVC, provides optimum resistance to aggressive weather conditions and guarantees that it will last for a long time.
Anti-UV soft PVC can be used for many applications but we recommend it for door and window applications, i.e. with rapid roller doors, marquee’s, tents or boat covers.
Applications



Why Use Anti-UV PVC?
Anti-UV PVC has been treated to resist the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight.
UV radiation can cause PVC to degrade over time, leading to discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical properties.
By incorporating UV stabilizers into the PVC formulation, we are able to extend the lifespan and maintain the appearance of PVC products exposed to sunlight, making them more durable and suitable for outdoor use.
Anti-UV flexible PVC can be used for many applications but is most commonly used for doors and window applications, i.e. with rapid roller doors, marquees, tents or boat covers.
Common application
- Tents and Marquees
- Roofing and Windows
- Medical Facilities
- Spray booths
- Boating and Yachting
- Tanning Salons


How work UV Absorbers ?
These additives work by absorbing UV radiation and converting it into harmless heat energy.
UV absorbers are typically organic molecules that are incorporated into the PVC formulation. When UV radiation strikes the PVC material, the UV absorbers absorb the radiation, preventing it from reaching the polymer chains and causing degradation.
Technical datasheet
| Properties | Standard | Units | Standard | Description |
| Light transmittance | ASTM D 1003 | % | 85 | Visible light rate transmitted through the material. |
| Shore A hardness | EN ISO 868 | Sh A | 80 | Index based on a flat indenter's penetration depth. Scale from 0 (Soft) to 100 (Hard). |
| Tearing resistance | DIN 53515 | N/mm | 50 | Minimum tensile stress required to tear a pre-slit sample. |
| Tensile strength at break | ASTM D 638 EN ISO 527 | N/mm² | 16 | Maximum tensile stress that a material can be subjected to before break. |
| Elongation at break | % | 340 | Elongation of the specimen at the break point under tensile stress. | |
| Residual elong. (after break) | % | 68 | Permanent elongation of the specimen measured after rupture in a tensile test. | |
| Thermal conductivity | ASTM C 177 | W/m.K | 0,16 | Ability to conduct heat. The lower it is, the more insulation. |
| Cold bend brittle temp. | ISO 8570 | °C | -35 | Temperature at which the specimen break under torsion stress. Brittle point (CLASH & BERG). |
| Min. usage temp. | EN 1876 | °C | -15 | Temperature range where material keeps its mechanical properties (flexibility). |
| Max. usage temp. | °C | +50 | ||
| Specific heat capacity | ISO 11357 | kJ/kg.K | 1,6 | Heat energy required to increase the temperature of one kilogram of the material by one degree Celsius. |
| Sound reduction | DIN 52210 | dB | >35 | Average sound level (freq. 0,1 to 3,2 kHz) decreased by a 1,76 sq.m. and 5 mm thick PVC curtain. |
| Reaction to fire | EN 13501-1 | Class | - | Standard classifications of material self-extinguishing and resistance to combustion. |
| UV/IR filter | ISO 25980 | - | - | Ability to filter welding rays allowing the use of this material as a welding protection screen. |
| UV resistance | ISO4892 | - | High | Ability to resist to UV (Sun, welding arc). |
| Surface resistivity | ASTM D257 | .1010 Ω/□ | 30 | Material surface electric resistivity measured with a 100 V direct voltage. |
| Water absorption | EN ISO 62 | % | -0,2 | Material mass variation after exposure to humid conditions. (<0 if released / >0 if absorbed) |
| Anti-insect | - | - | - | Special ability to keep insects away.(Food processing plants, tropical regions) |
| Density | ASTM D 792 | g/cm3 | 1,22 | Mass per unit volume. |
This information given to our customer in good faith to inform them and to help them in their search, does not constitute any formal or implicit guarantees as to its use.
Free download
- FLEXIBLE VINYL - NON-PHTHALATE PLASTICIZER (EN).pdf
- FLEXIBLE VINYL - SOLUTION FOR BUILDING (EN).pdf
- FLEXIBLE VINYL - SOUND REDUCTION (EN).pdf
- FLEXIBLE VINYL - THICKNESS & THERMAL INSULATION (EN).pdf
- FLEXIBLE VINYL - THERMAL INSULATION (EN).pdf
- FLEXIBLE VINYL - STABILIZERS & DURABILITY (EN).pdf
- PLASTIC MATERIALS & EARTH’S ENERGY RESOURCES (EN).pdf
- PLASTIC MATERIALS & GLOBAL WARMING (EN).pdf
- PLASTIC MATERIALS & OIL RESSOURCES (EN).pdf